04. Encoding the Board
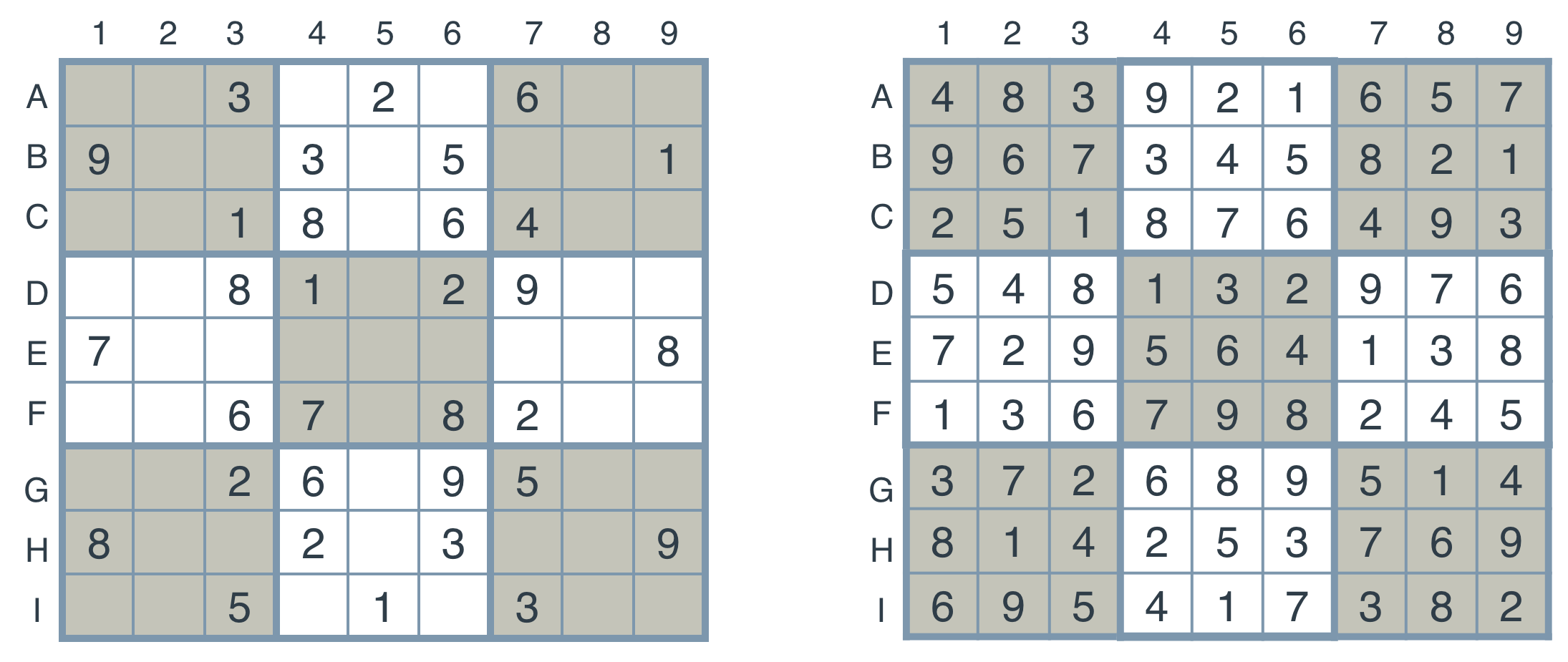
Now, in order to implement an agent, let's start by coding the board in Python. Then, we'll code the necessary functions to solve the Sudoku. We'll record the puzzles in two ways — as a string and as a dictionary.
The string will consist of a concatenation of all the readings of the digits in the rows, taking the rows from top to bottom. If the puzzle is not solved, we can use a . as a placeholder for an empty box.
For example, the unsolved puzzle at the above left will be written as:
..3.2.6..9..3.5..1..18.64....81.29..7.......8..67.82....26.95..8..2.3..9..5.1.3..
And the solved puzzle at the above right, will be recorded as:
483921657967345821251876493548132976729564138136798245372689514814253769695417382
We'll implement the dictionary as follows. The keys will be strings corresponding to the boxes — namely, 'A1', 'A2', …, 'I9'. The values will either be the digit in each box (if there is one) or a '.' (if not).
So, let's get started. First, we'll record rows and columns as strings.
rows = 'ABCDEFGHI'
cols = '123456789'We'll start by writing a helper function, cross(a, b), which, given two strings — a and b — will return the list formed by all the possible concatenations of a letter s in string a with a letter t in string b.
So cross('abc', 'def') will return ['ad', 'ae', 'af', 'bd', 'be', 'bf', 'cd', 'ce', 'cf'].
def cross(a, b):
return [s+t for s in a for t in b]Now, to create the labels of the boxes:
boxes = cross(rows, cols)
boxes =
['A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7', 'A8', 'A9',
'B1', 'B2', 'B3', 'B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7', 'B8', 'B9',
'C1', 'C2', 'C3', 'C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7', 'C8', 'C9',
'D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6', 'D7', 'D8', 'D9',
'E1', 'E2', 'E3', 'E4', 'E5', 'E6', 'E7', 'E8', 'E9',
'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6', 'F7', 'F8', 'F9',
'G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5', 'G6', 'G7', 'G8', 'G9',
'H1', 'H2', 'H3', 'H4', 'H5', 'H6', 'H7', 'H8', 'H9',
'I1', 'I2', 'I3', 'I4', 'I5', 'I6', 'I7', 'I8', 'I9']And for the units:
row_units = [cross(r, cols) for r in rows]
# Element example:
# row_units[0] = ['A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7', 'A8', 'A9']
# This is the top most row.
column_units = [cross(rows, c) for c in cols]
# Element example:
# column_units[0] = ['A1', 'B1', 'C1', 'D1', 'E1', 'F1', 'G1', 'H1', 'I1']
# This is the left most column.
square_units = [cross(rs, cs) for rs in ('ABC','DEF','GHI') for cs in ('123','456','789')]
# Element example:
# square_units[0] = ['A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']
# This is the top left square.
unitlist = row_units + column_units + square_unitsNow, we're ready to turn the string representation of a sudoku into a dictionary representation. That'll be your turn to shine!
Implement grid_values()
A function to convert the string representation of a puzzle into a dictionary form.
Recall that for the string:
'..3.2.6..9..3.5..1..18.64....81.29..7.......8..67.82....26.95..8..2.3..9..5.1.3..'…we'd like to return the dictionary:
{
'A1': '.'
'A2': '.',
'A3': '3',
'A4': '.',
'A5': '2',
...
'I9': '.'
}Implement a function called grid_values() that performs this task.
Following is an example of what you should see when you implement this function correctly. The display() function shows a nice visual representation of the dictionary, and has been provided in utils.py.
>>> from utils import display
>>> display(grid_values('..3.2.6..9..3.5..1..18.64....81.29..7.......8..67.82....26.95..8..2.3..9..5.1.3..'))
. . 3 |. 2 . |6 . .
9 . . |3 . 5 |. . 1
. . 1 |8 . 6 |4 . .
------+------+------
. . 8 |1 . 2 |9 . .
7 . . |. . . |. . 8
. . 6 |7 . 8 |2 . .
------+------+------
. . 2 |6 . 9 |5 . .
8 . . |2 . 3 |. . 9
. . 5 |. 1 . |3 . . Note:
- All your code should go in
function.py. - You can use the helper functions and variables defined in
utils.py. - Hit Test Run to execute your code and Submit to verify it against our grader.
- Once you're done, compare your implementation with ours in
solution.py.
Give it a shot!
Start Quiz:
User's Answer:
(Note: The answer done by the user is not guaranteed to be correct)